Get full access with a free account
Benefits of the Coloplast® Professional Educational platform
- Get full access to all educational content, events and resources
- Track your progress
- Share content with your collegues
- Share supporting material with your patient
Why is bladder microtrauma a problem for IC users?
A compromised bladder wall (epithelium) gives bacteria easy access to enter the epithelial cells and may increase the risk of UTIs.1
How does IC-related bladder microtrauma occur?
Mucosal suction is common when using conventional eyelet catheters1. The drainage of urine creates negative pressure inside the catheter that leads to the bladder mucosa getting sucked into the catheter eyelet in an abrupt and vigorous manner. This stops the urine flow, necessitating catheter repositioning, which may lead to scraping of the bladder mucosa.2
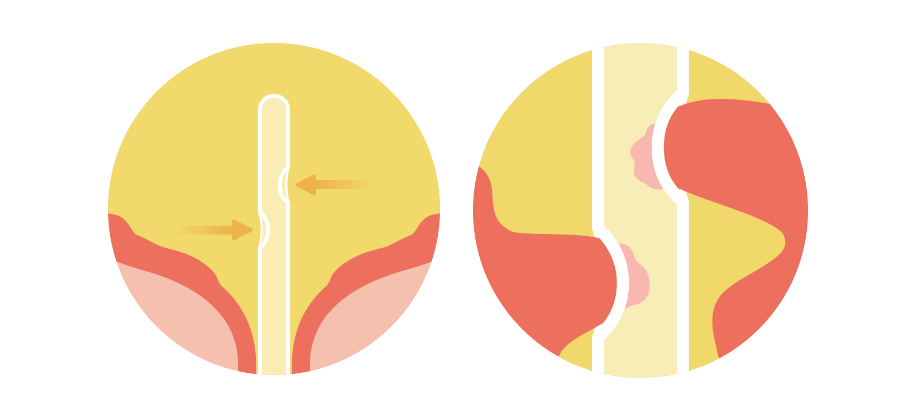
Eyelet blockage due to mucosal suction
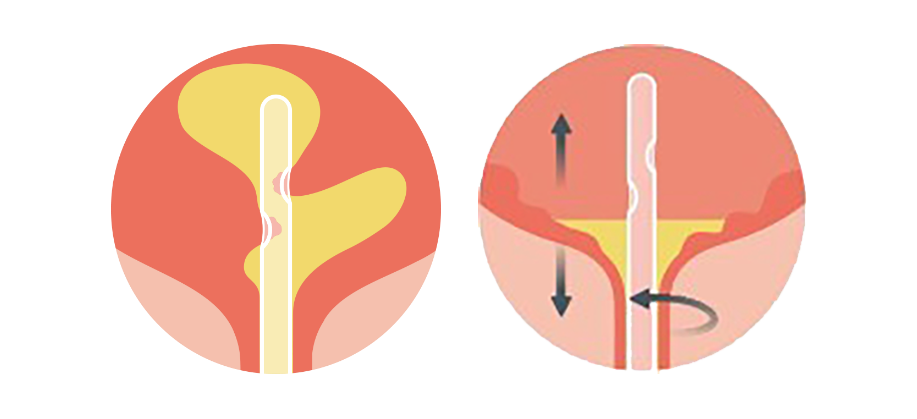
Repositioning required
The mucosal suction raises concerns for potential microtrauma, considering that 4–6 catheterisations are performed by an IC user daily.2
